When retrieving data from the internet, we often request entire web pages and extract the desired information by parsing HTML scripts. However, Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) offer a more efficient approach to accessing and retrieving data.
This tutorial aims to guide you through creating a self-contained application that utilizes an API to gather information and generate summaries based on that data. Specifically, we will focus on fetching information about Python projects from GitHub using the GitHub API. Additionally, we will demonstrate how to summarize the obtained information effectively.
Objectives
In this article we will go through:
Using an API call to request data.
Installation of
requestslibrary.Keeping track of an API response.
Using the response dictionary.
Summing up the top repositories.
Requesting data using an API call
GitHub’s web API allows you to make API requests for a range of data.
Type the following into your web browser URL bar and press Enter to see how an API call appears like:
https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=language:python&sort=stars
Let's break down the components of the API call:
The URL "api.github.com" is used to send the request to the GitHub web server specifically designed for handling API calls.
"
search/repositories" is the endpoint that instructs the API to search within all of GitHub's repositories.The "
?" symbol indicates that an argument is going to be passed to the API."
q=" signifies the start of the query parameter."
language:python" specifies that the API should search for repositories that primarily use Python as their programming language."
&sort=stars" indicates that the retrieved projects should be sorted based on the number of stars they have received.
Upon fetching the API data, the response will look like:

NOTE: The output above shows only the first few lines of the response.
Let’s examine the output:
In the second line of the result, you can see that GitHub has detected a total of
7668509Python projects.We know the request was successful if the value for
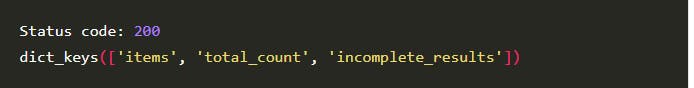
incomplete resultsisfalse.The key
itemsholds a list of objects that contains information of the Python-based projects on GitHub.
Let’s try to explore more information by parsing the API’s output using Python.
Installing requests
The requests package enables us to request data from the website and evaluate the result easily using a Python program.
Firstly, before starting with the installation process, make sure that Python and pip are installed before requests module installation.
To check if pip is installed,open the command prompt and run the following command pip --version
To install therequests library for Python, we have to navigate to the Python directory,
Example C:\Users\USER\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python310\Lib and then install the request module as follows:
python -m pip install requests
Processing an API response
To fetch the most starred Python projects on GitHub, we’ll start writing a program that will make an API call and evaluate the data as shown:
import requests
# Create an API request
url = 'https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=language:python&sort=stars'
response = requests.get(url)
print("Status code: ", response.status_code)
# In a variable, save the API response.
response_dict = response.json()
# Evaluate the results.
print(response_dict.keys())
Let’s understand the code snippet above:
We begin by importing the
requestsmodule.Then, we use the
requestspackage to make the API call to the particularurlusingget().The API response is saved by a variable called
response.The
status_codeattribute of theresponseobject indicates if the request was complete.A successful API call returns the
status_code200, while an unsuccessful one returns500.Then, we use the
json()function to convert the information from JSON format to a Python dictionary.We store the converted JSON in
response_dict.
Then, we print the keys from response_dict, which are as follows:
Using the response dictionary
Now, let’s make a report that sums up all the information.
Here, we will be calculating the total number of available repositories with language as Python, and fetch all the keys under items as shown:
import requests
# Make an API call
url = 'https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=language:python&sort=stars'
j = requests.get(url)
print("Status code:", j.status_code)
# In a variable, save the API response.
respons_dict = j.json()
print("Total repositories:", respons_dict['total_count'])
# Explore information about the repositories.
repos_dicts = respons_dict['items']
print("Repositories found:", len(repos_dicts))
# Examine the first repository.
repos_dict = repos_dicts[0]
print("Keys:", len(repos_dict))
for key in sorted(repos_dict.keys()):
print(key)
Let’s understand the code snippet above:
The value linked with the
total_countreflects the count of GitHub Python projects available.The value of
itemsis a list of dictionaries, each providing information about a single Python repository.The list of dictionaries is then saved in
repos_dicts.We select the first item from
repos_dictsto look more closely at the information given about each repository.Finally, we print the all of keys of an
item.
Below is the output:
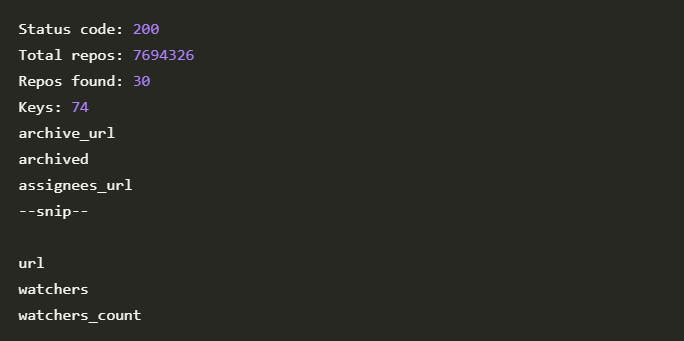
The GitHub API gets back a range of data for every repository like:
status_codeas200.Total number of repos as
7694326.Total number of repos found as
30.Each repository
repo_dicthaving74keys.
You may get a sense of the type of information you can get about a repository by observing these keys.
Let’s have a look at what some of the keys in repo _dict entail:
## Make an API call
url = 'https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=language:python&sort=stars'
j = requests.get(url)
print("Status code:", j.status_code)
# Store API response in a variable.
respons_dict = j.json()
print("Total repositories:", respons_dict['total_count'])
# Explore information about the repositories.
repos_dicts = respons_dict['items']
print("Repositories returned:", len(repos_dicts))
# Examine the first repository.
repos_dict = repos_dicts[0]
print("\nThe following is some information regarding the first repository:")
print('Name:', repos_dict['name']) #print the name of the project
print('Owner:', repos_dict['owner']['login']) #use the key owner and the the key login to access the dictionary representing the owner and the owner’s login name respectively.
print('Stars:', repos_dict['stargazers_count']) #print how many stars the project has earned
print('Repository:', repos_dict['html_url']) #print URL for the project’s GitHub repository
print('Created:', repos_dict['created_at']) #print when it was created
print('Updated:', repos_dict['updated_at']) #show when it was last updated
print('Description:', repos_dict['description']) #print the repository’s description
Output:
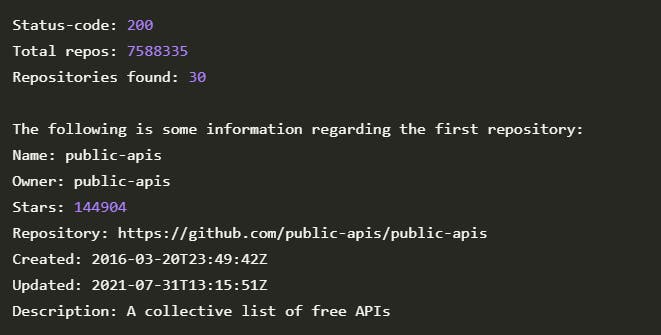
Examining the output:
You can observe that the most popular Python repository on GitHub is
public-apis.Owner of the repository is
public-apis.It has been starred more than
140,000times.Project was created on the date of
2016 March.Project description of
public-apisiscollective collection of open APIs.
Sum top repositories
To analyze multiple repositories obtained from the API call, we can create a loop that prints specific information about each repository. The loop will iterate over the repositories and extract the desired information. By doing this, we can analyze and display information about each repository individually.
import requests
url = 'https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=language:python&sort=stars'
r = requests.get(url)
print("Status code:", r.status_code)
respons_dict = r.json()
print("Total repositories:", respons_dict['total_count'])
repos_dicts = respons_dict['items']
print("Repositories returned:", len(repos_dicts))
print("\nSelected information about each repository:")
for repos_dict in repos_dicts: #loop through all the dictionaries in repo_dicts.
print('\nName:', repos_dict['name'])
print('Owner:', repos_dict['owner']['login'])
print('Stars:', repos_dict['stargazers_count'])
print('Repository:', repos_dict['html_url'])
print('Description:', repos_dict['description'])
Output:
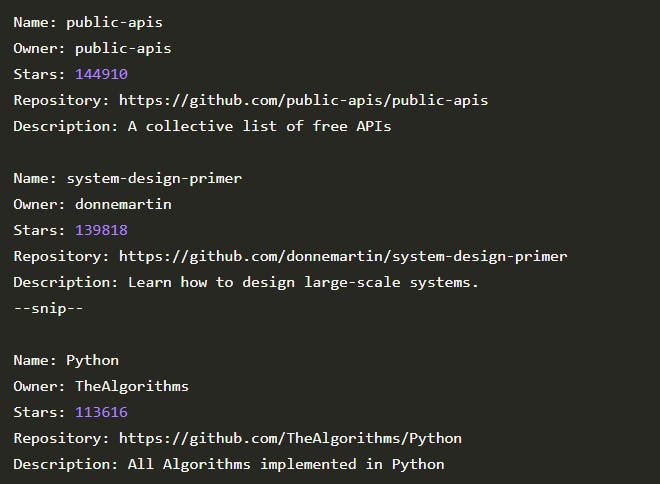
We print the name of each project, its owner, the number of stars it has, its GitHub URL, and the project’s description inside the loop:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have gone over the following:
Using an API call to request data.
Installing requests.
Processing an API response.
Using the response dictionary.
Summing up the top repositories.
Happy coding!
